Which Blood Cell Lacks a Nucleus
Explore the definition function and types of cell bodies and learn about neurons. 412 The cell theory In 1838 MJ.
Why Don T Matured Human Rbcs Have A Nucleus Quora
We would like to show you a description here but the site wont allow us.
. The blood-testis barrier BTB is one of the tightest blood-tissue barriers in the mammalian body. In eukaryotic cells all the chromosomes are contained within the nucleus. It appears dumbbell-shaped in profile.
As a senior investigator at the UCSF-affiliated Gladstone. Nucleus is bilobed two lobes Basophil. Schleiden and Theodore Schwann formulated the cell theory.
Electron microscopic examinations of cell membranes have led to the development of the lipid bilayer model also referred to as the fluid-mosaic model. It divides the seminiferous epithelium into the basal and the apical adluminal compartments. Insofar as it contains a nucleus every cell during development carries the totality of all primordia.
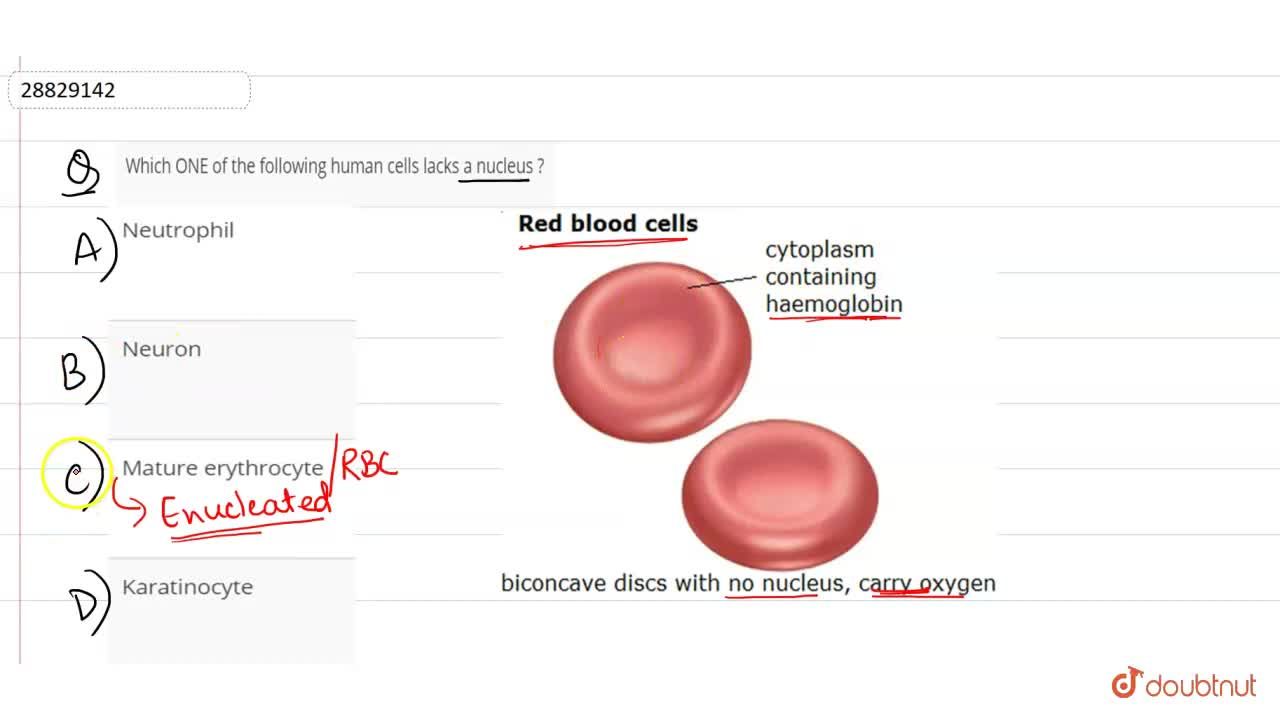
Much later in 1831 Robert Brown an Englishman observed that all cells had a centrally positioned body which he termed the nucleus. The key difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and membrane-bound organelles whereas prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus. It is covered with a membrane composed of lipids and proteins lacks a nucleus and contains hemoglobina red iron-rich protein that binds.
People with type AB blood are considered the universal recipient for transfusions because A their blood cells lack A and B antigens. Antigens are molecules such as proteins lipids carbohydrates or nucleic acids that your body can use to differentiate self and non-self. Nucleus is bean or C shapedMonocyte 4.
Antibodies are produced in response to some. People with different blood types have different antigens on their RBCs. He serves as the director of Center for iPS Cell induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Research and Application and a professor at the Institute for Frontier Medical Sciences at Kyoto University.
Insofar as it contains a specific cytoplasmic cell body it is specifically enabled by this to respond to specific effects onlyWhen nuclear material is activated then under its guidance the cytoplasm of its cell that had first influenced the nucleus is in turn changed and thus the. Red blood cells are the major cellular component of blood. The coagulation common pathway ends with the formation of an insoluble _____ polymer that will serve as the framework.
The cell body also known as the soma is the part of a neuron that contains the nucleus and controls cell function. Mature red blood cells are biconcave discs that lack nucleus and most cell organelles such as lysomes endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. Leeuwenhoek observed bacteria sperms and red blood corpuscles all of which were cells.
Blood type refers to the presence or absence of specific molecules called antigens on the red blood cell RBC RBC surface. Large cell twice as big as a red blood cell. Meiosis I and II spermiogenesis and spermiation all take place in a specialized microenvironment behind the BTB in the apical compartment but spermatogonial renewal and differentiation and.
ALCL primarily involves lymph nodes and skin but particularly in the small-cell variant may demonstrate peripheral blood involvement. The cell is flexible and assumes a bell shape as it passes through extremely small blood vessels. The mature human red blood cell is small round and biconcave.
Nucleus is bilobed two lobes Eosinophil 5. The cell membrane functions as a semi-permeable barrier allowing a very few molecules across it while fencing the majority of organically produced chemicals inside the cell. Cell is full of dark-purple staining granules.
C their blood is plentiful in A and B agglutinins. 87 ALCL is usually CD4 may express CD56 is most frequently CD2 but often lacks many other T-cell antigens including CD3 CD5 and CD7 and may express the myeloid associated antigens CD13 CD15 and CD33. In prokaryotic cells the chromosome is located in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid which lacks.
D they usually have very strong immune systems. Shinya Yamanaka 山中 伸弥 Yamanaka Shinya born September 4 1962 is a Japanese stem cell researcher winner of the Nobel Prize. E they are usually Rh negative.
B their blood lacks A or B agglutinins. Cell full of red-pink staining granules.

Do Red Blood Cells Have A Nucleus Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

No comments for "Which Blood Cell Lacks a Nucleus"
Post a Comment